DC-DC boost converters, also known as DC boost choppers, are DC-DC converters that can boost the voltage so that the output (load) voltage is higher than the input (power) voltage. Boost converters are switching power supplies with at least two semiconductor elements (a diode and a transistor) and at least one energy storage element (inductor). To reduce voltage ripple, filters made of capacitors (sometimes with inductors) are added at the input and output.
DC-DC boost converters can be powered by any suitable DC power source, such as batteries, solar panels, rectifiers or DC generators, etc. DC-DC converters can convert DC power of a certain voltage to DC power of a different voltage. DC boost converters are DC-DC converters that will increase the voltage, and their output voltage will be higher than the input voltage. However, because power must be conserved, the output current will be less than the input current, even under the assumption of 100% efficiency.
The invention of commercial semiconductor switches in the 1950’s was very important for switching power supplies, so that switching power supplies such as boost converters could be implemented. The major DC-DC converter technology was developed in the early 1960’s when semiconductor switches became available. The aerospace industry needed small, lightweight and highly efficient power converters, so switching power supplies developed rapidly.
Application
A DC-DC boost converter on a computer can boost power from 2.4 V supplied by two batteries to 9 V. Battery-powered systems typically connect batteries in series to bring up higher voltages, although in many high-voltage applications, space constraints prevent the use of enough batteries in series to bring up the required voltage. Boost converters can boost the voltage and reduce the number of batteries required. Systems such as electric vehicles and lighting systems are systems that use batteries in combination with boost converters to supply power.
Hybrid cars use a 500 V electric motor, without a boost converter, it would take nearly 417 batteries to drive the motor, but some cars only use 168 batteries, and then use a DC-DC boost converter to raise the total battery voltage from 202 V to 500 V. DC-DC boost converters can also be used to power some smaller devices, such as portable lighting systems, like White LEDs generally need 3.3 V to emit light, and with the boost converter can use the 1.5 V voltage provided by the alkaline battery, and then step up the voltage to supply power.
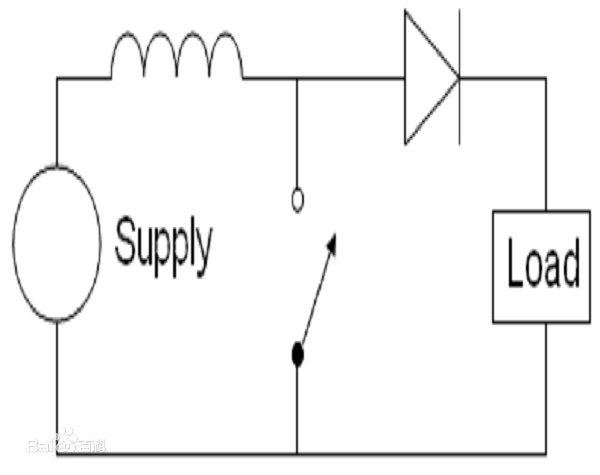
A circuit called the Joule thief uses an unregulated DC-DC boost converter as a boosting mechanism. This circuit architecture is used in low-voltage battery applications and is designed to use a DC-DC boost converter to obtain residual power from the battery. When the battery is almost dead, the residual power of the battery is wasted because the voltage is not enough to drive the general load.